Cytovaricin
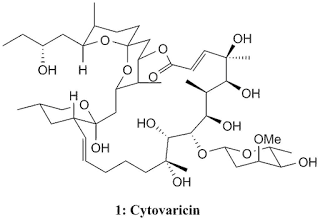
Cytovaricin, 1 , was isolated by Isono's group in 1981 from a culture of Streptomyces diastatochromogenes and the structure was elucidated in 1983 from X-ray crystallography. From its structure, cytovaricin was revealed to have such an elegant and complex structure with 22-membered macrolide structure as its framework and possessing 17 stereocentres, a spiroketal, and a glycoside unit giving four more stereocentres. This highly complex molecule give a unique challenge to organic chemists in asymmetric synthesis. The structure elucidation of cytovaricin was triggered from the finding that it is a potent inhibitor against sarcoma cells in tissue culture which makes cytovaricin a new potential as antineoplastic antibiotic. Besides that, cytovaricin appears to be related biogenetically to the oligomycin/rutamycin antibiotic family.

